Brave Search (From Brave Browser) Introduces Brave Summarizer, an AI Tool for Synthesized Results
From the Product Release Announcement:
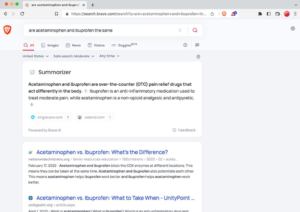
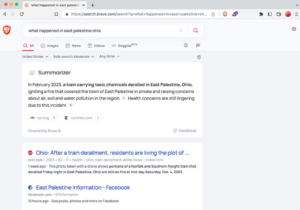
The Summarizer provides concise and to-the-point answers at the top of Brave Search results pages, in response to the user’s input, solely based on Web search results. Unlike a purely generative AI model, which is prone to spout unsubstantiated assertions, we trained our large language models (LLMs) to process multiple sources of information present on the Web. This produces a more concise, accurate answer, expressed in coherent language.
In addition, the provenance of original sources of data is cited at all times via links. This maintains the rightful attribution of information, and helps users assess the trustworthiness of the sources, both of which are needed to mitigate the authority biases of large language models.
[Clip]
The Brave Summarizer is available today for all users of Brave Search, on desktop and mobile. For users who would prefer not to use the Summarizer, they can easily turn it off by opting out in settings.
[Clip]
Besides the summary itself, our AI models are also able to replace the already query-dependent snippets (result descriptions) with a summarized version of those snippets, highlighting the answer when possible. This can be viewed as a summary of a single source (such as a press article), as opposed to the main summary where multiple sources are considered and aggregated to create a more comprehensive answer. The summary at the top of the results page and these special descriptions co-occur, so users will see the overarching summary as well as snippets with highlighted answers.
[Clip]
The Summarizer was fully developed by the Brave Search team and as such is based on the same principles of independence and privacy that we apply across all products. The Summarizer is not powered by ChatGPT or its backend systems; it is instead composed of three different LLMs trained on different tasks:
- The first one is QA (question answering): this model is used to try to extract a concrete answer, if any, from text snippets. Brave has been using LLMs for a while to improve search relevance, and this is an extension of what Brave Search already had in place to power its knowledge graph and featured snippets features. The difference lies in the number and length of text snippets analyzed.
- After the QA extraction phase, result candidates are further classified with an ensemble of zero-shot classifiers on a wide variety of criteria (hate-speech, vulgar writing, spam, etc).
- The final set of candidate text is ultimately processed by the summarizer/paraphrasing model, which tries to rewrite the input so that repetition is removed and that language is kept uniform to improve readability.
Learn More, Direct to Complete Launch Announcement
Direct to Brave Search
Filed under: Data Files, News, Patrons and Users
About Gary Price
Gary Price (gprice@gmail.com) is a librarian, writer, consultant, and frequent conference speaker based in the Washington D.C. metro area. He earned his MLIS degree from Wayne State University in Detroit. Price has won several awards including the SLA Innovations in Technology Award and Alumnus of the Year from the Wayne St. University Library and Information Science Program. From 2006-2009 he was Director of Online Information Services at Ask.com.